


Next: Compositional Differences
Up: Gene Finding
Previous: Prokaryotes
Finding Long ORF's
One way to distinguish coding regions from non-coding regions, is to look at the
frequencies of stop codons. Assuming a uniform random
distribution, a stop codon is expected to be observed every
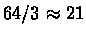 codons (since there are 3 stop codons). Average proteins are much
longer, being coded for by about 1000bp (base pairs). Each coding
region has only one stop codon, which terminates the region.
Therefore, one way to detect the coding regions, is to look for
long sequences of codons, without any stop codon.
The algorithm that uses the above idea, scans the DNA sequence, looking for long ORF's
in all three reading frames. After detecting a stop codon, the algorithm scans backward,
searching for a start codon.
This algorithm will fail to detect very short genes, and also
won't identify overlapping long ORFs on opposite strands.
codons (since there are 3 stop codons). Average proteins are much
longer, being coded for by about 1000bp (base pairs). Each coding
region has only one stop codon, which terminates the region.
Therefore, one way to detect the coding regions, is to look for
long sequences of codons, without any stop codon.
The algorithm that uses the above idea, scans the DNA sequence, looking for long ORF's
in all three reading frames. After detecting a stop codon, the algorithm scans backward,
searching for a start codon.
This algorithm will fail to detect very short genes, and also
won't identify overlapping long ORFs on opposite strands.
Itshack Pe`er
1999-02-03