


Next: Functional Analysis
Up: Preface
Previous: Preface
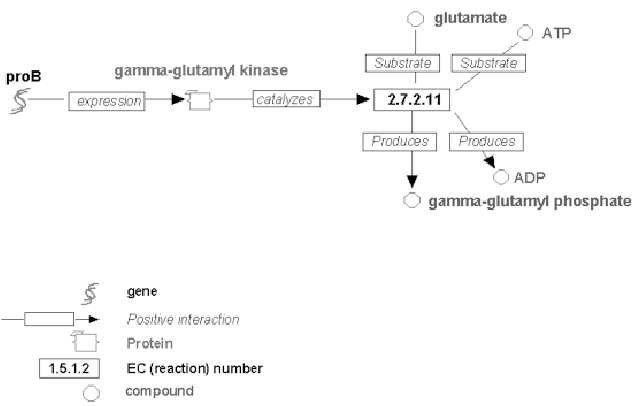
Figure 14.1 depicts gene expression and its role in
catalyzing certain chemical reaction in the cell. The proB gene is
being expressed into the gamma-glutamyl-kinase protein, which
catalyzes a reaction involving glutamate and ATP, which produces
gamma-glutamyl-phosphate and ADP compounds.
Figure 14.1:
An example for the role of gene expression in catalyzing
chemical reactions.
 |
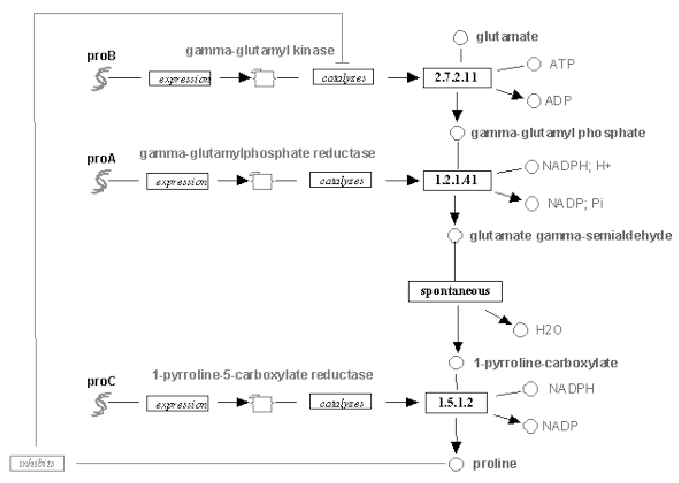
This gene expression is a part of a simple metabolic pathway,
involving a chain of generated proteins, which is shown on figure
14.2. One of the final products of the chain,
proline, inhibits the initial reaction, which has started the
whole process. This "feedback inhibition" pattern is highly
typical to genetic networks, and serves to regulate the process
execution rate.
Figure 14.2:
An example of an metabolic pathway: Proline
biosynthesis.
 |
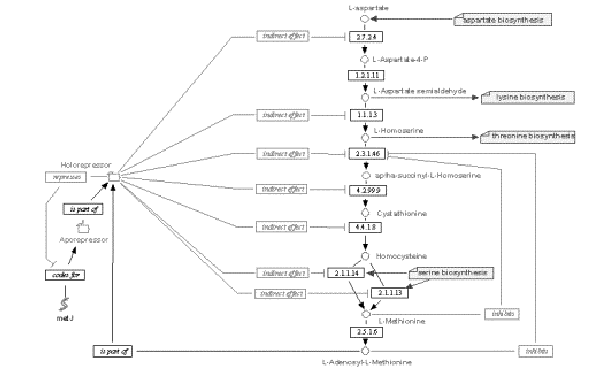
The following two figures show a more complex gene network, describing
Methionine biosynthesis in E-coli. The second figure is a shortcut
representation of the pathway, with most nodes omitted, but it can give
a better idea on overall topology.
Figure 14.3:
Methionine biosynthesis network in E-coli.
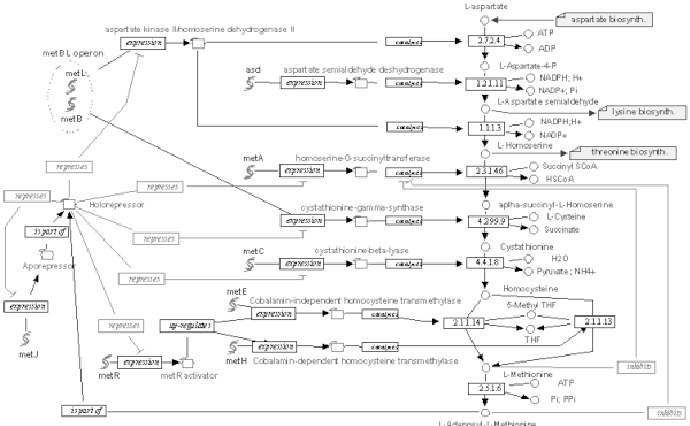 |
Figure 14.4:
Shortcut representation of the biosynthesis pathway
presented in Figure 14.3
 |
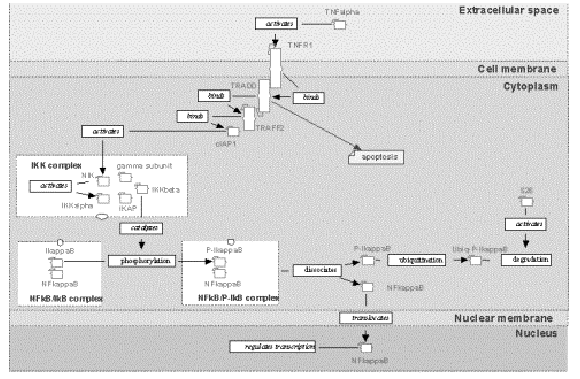
The last example is that of signal transduction - complex cellular
process initiated by signaling protein arrived from outside of a cell.
This process eventually affects gene expression in the cytoplasm and inside
the nucleus.
Figure 14.5:
A gene network that performs signal transduction from
outside the cell into the nucleus.
 |



Next: Functional Analysis
Up: Preface
Previous: Preface
Peer Itsik
2001-03-04

