Counters
Types:
- Synchronous counter
- Ripple counter
- Synchronous counter: All the flip-flops are fed from the input clock.
- Ripple counter: Cascade connection of Flip-Flops (each FF feeds the clock of the following FF).
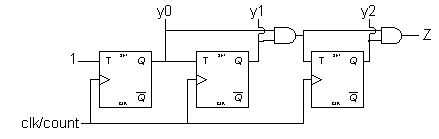
We want to count 8 states ---> we need 3 FF to hold the states 2^3=8. States – Y0, Y1, Y2
State table:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Implementation:
y1 y2
_______________________
| | 00 01 11 10 t0 = y1y1
|---|------------------
y0 | 0 | 0 0 1 0
| 1 | 0 0 1 0
y1 y2
_______________________
| | 00 01 11 10 t1 = y0
|---|------------------
y0 | 0 | 0 1 1 0
| 1 | 0 1 1 0
y1 y2
_______________________
| | 00 01 11 10 t2 = 1
|---|------------------
y0 | 0 | 1 1 1 1
| 1 | 1 1 1 1
Z=y2 y1 y0 because it
gets 1 only when y0, y1, y2 are 1.
Creating a mod 64 counter from two mod 8 counters:

- Control bit U/D` - U/D` = 1 --> up-counter
- U/D` = 0 --> down-counter
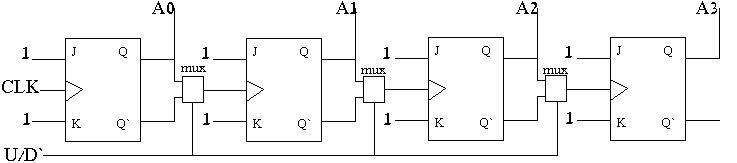
Implementing up/down counter:

- x=0 up counter
- x=1 down counter
----------
a= 0 0
b= 0 1
c= 1 0
d= 1 1
y1 y0
x Y1 Y0
-----------------------------------
0
0 0 0
1
0
0 1 1
1
0
1 0 1
0
0
1 1 0
0
1
0 0 1
1
1
0 1 0
1
1
1 0 0
0
1
1 1 1
0

y0 x
____________________
|
| 00 01 11 10
|--- |----------------------
y1 | 0 | 1
1 1 1
| 1 |
0 0 0
0
t0=y0'
y0 x
____________________
|
| 00 01 11 10
|--- |----------------------
y1 | 0 | 0
1 0 1
| 1 |
1 0 1
0
t1=y0 xor y1 xor x
Decimal counter: ( Non synchronized)
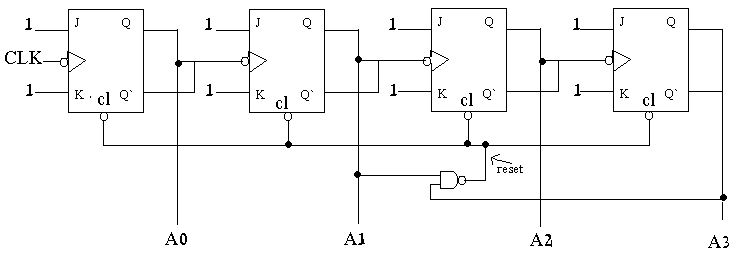
It is also easy to construct synchronized decimal
counter
Timing diagram:

Divider by n:
Every n rises of the input clock, the
divider gives a single rise at the output.
Divider by 2:
Divider by 4:
